
Data science has revolutionized how business is done today, and in every case, the business insights offered by data analytics have enabled companies to modernize their workflows, so that every data point can be better tracked. Retail, supply chain and logistics industries that interplay to benefit each other demonstrate how data science, analytics and AI have been able to transform them. The retail supply chain is complex, and many of its key interactions used to be documented either manually or with primitive technologies. But with the advancement of data science, it has become easier to pour through the data to analyze and generate actionable insights for brands in both the retail, supply chain and logistics industries.
Today, data science has made a mark on just about every aspect of retail, supply chain and logistic businesses, including marketing strategy, supply chain management, digital transformation processes. In this article, we’re going to take a look at specific USE CASE examples from various companies on multiple dimensions where data science has transformed approaches and produced meaningful insights for both retail and logistics industry that are inter-dependent for their successes.

LOGISTICS and SUPPLY CHAIN INDUSTRY
1. Behavior Analysis:
- Use Case Example: DHL
- Description: DHL uses behavior analytics to track the movement of packages and shipments in real-time.
- Impact: This helps optimize routing, identify bottlenecks, and improve the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
2. Customer Experience:
- Use Case Example: FedEx
- Description: FedEx utilizes data science to provide customers with real-time tracking information and delivery updates.
- Impact: Enhances customer satisfaction by providing transparency and a better overall delivery experience.

3. Trend and Sales Forecasting:
- Use Case Example: UPS
- Description: UPS employs data science for trend analysis and sales forecasting in the logistics industry.
- Impact: Helps anticipate fluctuations in demand, optimize inventory levels, and improve resource allocation.
4. Recommendation Engines:
- Use Case Example: Amazon Logistics
- Description: Amazon Logistics uses recommendation engines to optimize delivery routes for its drivers.
- Impact: Improves delivery efficiency, reduces fuel consumption, and minimizes the environmental impact.

5. Customer Segmentation:
- Use Case Example: Maersk
- Description: Maersk, a shipping company, uses customer segmentation to tailor services for different client types.
- Impact: Enhances customer satisfaction by providing customized solutions for various shipping needs.
6. Inventory Management and Optimization:
- Use Case Example: XPO Logistics
- Description: XPO Logistics utilizes data science for inventory optimization, ensuring the right levels of stock at distribution centers.
- Impact: Reduces holding costs, minimizes stockouts, and streamlines the supply chain.
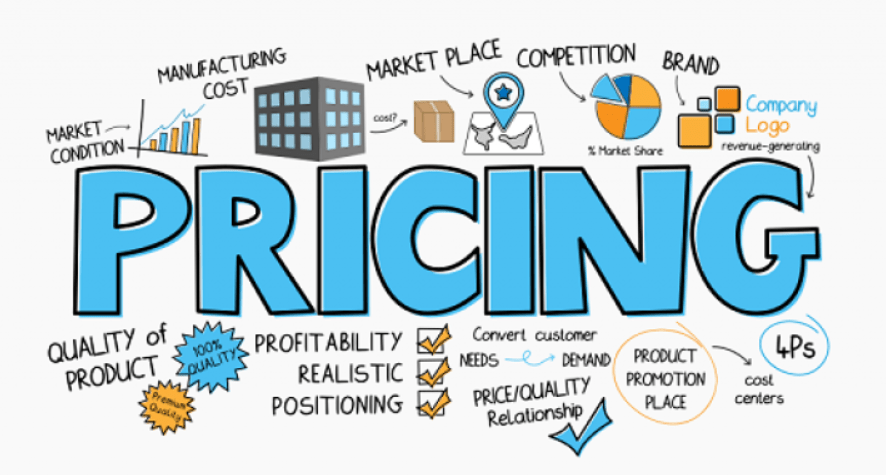
7. Price Optimization:
- Use Case Example: C.H. Robinson
- Description: C.H. Robinson employs data science for dynamic pricing in freight and transportation services.
- Impact: Maximizes revenue by adjusting pricing based on real-time market conditions and demand.
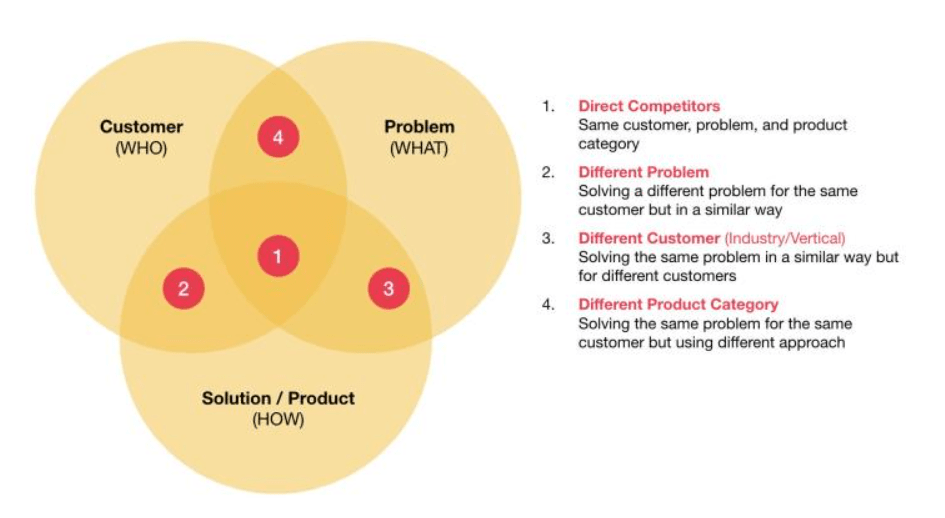
8. Competitor Analysis:
- Use Case Example: Dicom Transportation Group
- Description: Dicom Transportation Group uses data science to analyze competitor pricing, service offerings, and market positioning.
- Impact: Helps make strategic decisions and stay competitive in the logistics market.
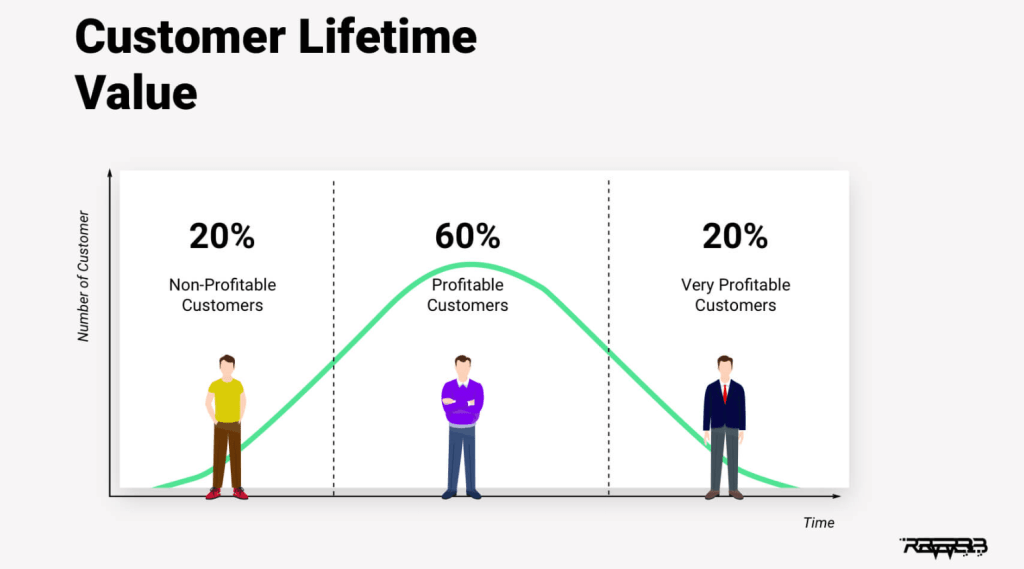
9. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV):
- Use Case Example: DB Schenker
- Description: DB Schenker employs data science to predict customer lifetime value and tailor services for long-term clients.
- Impact: Enhances customer retention and loyalty by offering personalized solutions and services.
10. Fraud Detection:
- Use Case Example: Flexport
- Description: Flexport uses data science for fraud detection in international shipping and logistics.
- Impact: Enhances security, prevents fraudulent activities, and maintains trust in the logistics platform.

11. Predictive Maintenance:
- Use Case Example: Maersk Line
- Description: Maersk Line employs data science for predictive maintenance of its fleet.
- Impact: Reduces downtime and maintenance costs by predicting when vessels and equipment need attention.
12. Better Decision-Making:
- Use Case Example: DHL Supply Chain
- Description: DHL Supply Chain uses data-driven decision-making for route optimization, warehouse management, and resource allocation.
- Impact: Improves overall logistics efficiency and enhances decision-making processes.
These examples illustrate how data science is integral to the logistics and supply chain industry, driving improvements in efficiency, customer satisfaction, and strategic decision-making. Companies in this sector continue to leverage data analytics and AI to stay competitive and deliver high-quality services to clients.

RETAIL INDUSTRY:
1. Behavior Analytics:
- Use Case Example: Amazon
- Description: Amazon utilizes behavior analytics to track customer browsing and purchasing behavior on its platform.
- Impact: By analyzing user behavior, Amazon provides personalized product recommendations, improving the overall shopping experience and increasing sales.
2. Customer Experience:
- Use Case Example: Sephora
- Description: Sephora employs data science to enhance the in-store and online customer experience.
- Impact: Virtual try-on tools, personalized product recommendations, and tailored promotions contribute to a more engaging and satisfying customer experience.
3. Trend and Sales Forecasting:
- Use Case Example: Zara
- Description: Zara uses data science to analyze fashion trends and forecast demand.
- Impact: This enables Zara to quickly adapt its inventory, ensuring that popular items are in stock and reducing the risk of overstocking less trendy products.
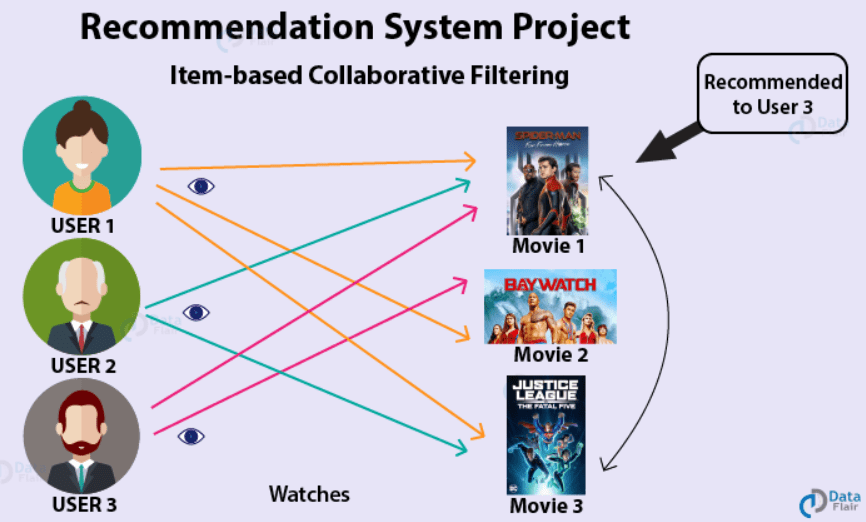
4. Recommendation Engines:
- Use Case Example: Netflix
- Description: Netflix employs recommendation engines based on user viewing history and preferences.
- Impact: By suggesting personalized content, Netflix keeps users engaged, leading to increased customer satisfaction and retention.
5. Customer Segmentation:
- Use Case Example: Starbucks
- Description: Starbucks uses customer segmentation through its loyalty program and mobile app.
- Impact: By understanding customer segments, Starbucks tailors promotions and offers, improving customer loyalty and increasing average transaction value.

6. Inventory Management and Optimization:
- Use Case Example: Walmart
- Description: Walmart employs data science to optimize inventory levels across its extensive supply chain.
- Impact: Efficient inventory management reduces holding costs, minimizes stockouts, and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
7. Price Optimization:
- Use Case Example: Airlines (e.g., Indigo, Air India, Delta, American Airlines)
- Description: Airlines use dynamic pricing algorithms based on factors like demand, time of booking, and historical data.
- Impact: Maximizes revenue by adjusting ticket prices dynamically, responding to market conditions and customer behavior.
8. Competitor Analysis:
- Use Case Example: Target
- Description: Target uses data science to analyze competitor pricing, promotions, and customer preferences.
- Impact: Helps Target make strategic pricing decisions, stay competitive, and attract customers with targeted promotions.
These examples illustrate how data science is integral to the retail industry, driving improvements in efficiency, customer satisfaction, and strategic decision-making. Companies in this sector continue to leverage data analytics and AI to stay competitive and deliver high-quality services to customers.

